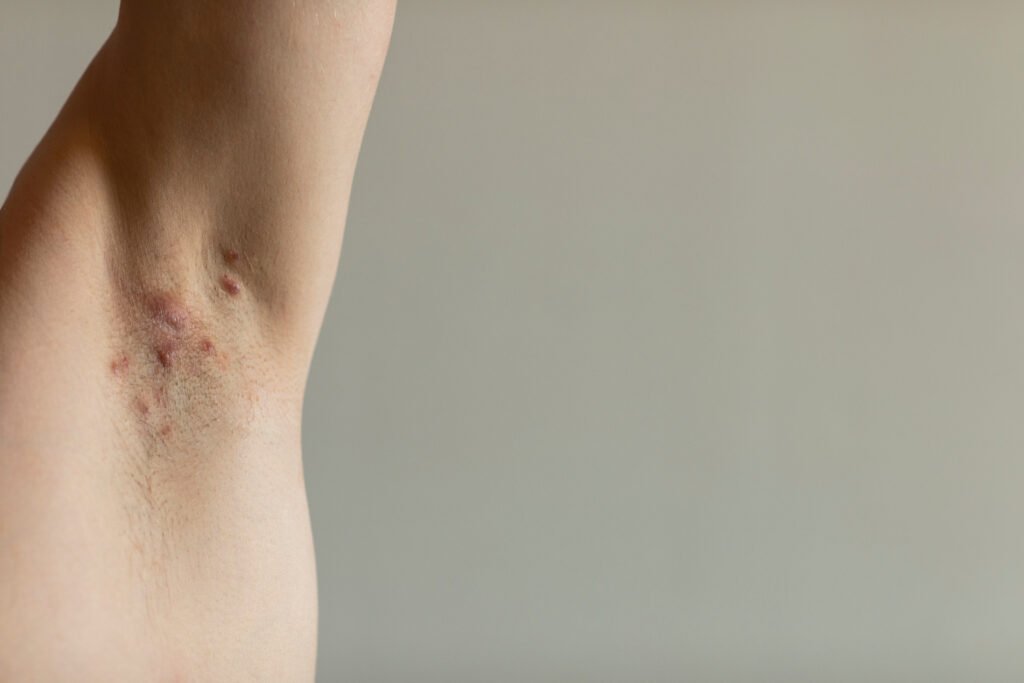
When hidradenitis suppurativa treatments fail, patients face the devastating reality that their carefully managed condition may spiral out of control, leaving them desperate for alternatives that medical professionals rarely discuss.
Story Overview
- HS treatment failure affects up to 40% of patients within two years of starting therapy
- Secondary treatment options exist but require aggressive advocacy and specialist consultation
- Lifestyle modifications can provide substantial relief when medications plateau
- Support networks become crucial for navigating treatment-resistant cases
The Treatment Plateau Reality
Hidradenitis suppurativa patients often experience what dermatologists call “treatment escape” – a phenomenon where previously effective medications gradually lose their impact. This occurs because HS involves complex inflammatory pathways that can adapt and circumvent single-target therapies. The condition’s progressive nature means that what controls symptoms today may prove inadequate tomorrow, leaving patients watching helplessly as their carefully managed disease regains momentum.
Watch: When Your HS Treatments Stop Working: Finding New Paths to Relief
Beyond First-Line Failures
When antibiotics and topical treatments stop working, most patients assume they’ve exhausted their options. However, several advanced therapies remain underutilized in clinical practice. Biologic medications like adalimumab and infliximab target specific inflammatory proteins, offering hope for antibiotic-resistant cases. Surgical interventions, including wide excision and laser therapy, can eliminate affected tissue entirely. These options require specialized care but provide genuine alternatives when conventional treatments plateau.
The challenge lies in accessing these advanced treatments. Many dermatologists lack experience with severe HS cases, leading to delayed referrals to specialists who understand the condition’s complexity. Patients must advocate aggressively for comprehensive evaluation and refuse to accept treatment failure as inevitable.
The Lifestyle Medicine Approach
Research increasingly demonstrates that HS responds significantly to targeted lifestyle interventions, particularly when pharmaceutical approaches stagnate. Anti-inflammatory diets, specifically those eliminating dairy, refined sugars, and nightshade vegetables, can reduce flare frequency by up to 60% in some patients. Weight management becomes crucial, as excess adipose tissue creates the warm, moist environments where HS bacteria thrive.
Stress reduction through meditation, adequate sleep, and exercise modifications also plays a documented role in symptom management. These interventions work synergistically with medical treatments, often restoring effectiveness to previously failed medications. The key involves implementing multiple strategies simultaneously rather than relying on single interventions.
Building Your Treatment Team
Treatment-resistant HS requires a multidisciplinary approach that extends beyond dermatology. Endocrinologists can address hormonal triggers, particularly in women whose symptoms fluctuate with menstrual cycles. Pain management specialists help develop comprehensive strategies for chronic discomfort. Mental health professionals provide essential support for the psychological burden of living with a visible, painful condition.
Patient advocacy groups and online communities offer practical insights that medical professionals often miss. These networks share real-world experiences with emerging treatments, lifestyle modifications, and specialist recommendations. However, patients must balance community advice with professional medical guidance, ensuring that alternative approaches complement rather than replace evidence-based care.